
But, divers can also encounter a 'reverse squeeze' on the way back up to the surface.įactors that often create equalisation problems for scuba divers include: It happens most often during abrupt pressure changes, such as when descending. In most cases, this 'blockage' is likely to be a contributing factor for MEBT. In simple terms, any kind of obstruction in the eustachian tube reduces a diver's ability to achieve equalisation.

So, why do some divers suffer this medical complication more than others?


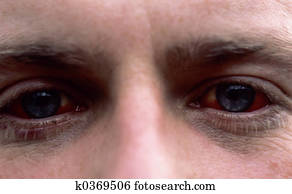
Health surveys suggest middle-ear barotrauma affects around 80% of divers at some time or another. But, failing to equalise the pressure in the air space of the middle ear with the surrounding pressure (ambient) is a frequent cause of MEBT - especially with inexperienced divers. No matter whether you're a beginner or a professional, equalizing pressure while diving is a fundamental part of the process. Whereas, the canals contribute some control over the way we balance and position ourselves. The cochlea converts soundwaves into electrical impulses for the brain. Note: The inner ear forms part of the central nervous system and has two main functions. Inner Ear: The labyrinth is a sensory organ for balance and hearing.Middle Ear: The air-filled cavity positioned between the eardrum and the inner ear also has three components, namely the middle-ear cavity, the ossicles (three tiny bones) and the mastoid process.External Ear: This segment contains the actual ear itself, as well as the ear canal (which leads to the eardrum).Human ears contain three distinct sections, and each component has a different purpose: Antivertigo medications (e.g.Anatomy of the Human Ear and its Function.Urgent audiology required if sensorineural hearing loss, rather than conductive hearing loss.Remember to use medications such as ofloxacin suspension that will be safe in the middle ear.Consider antibiotics if tympanic membrane rupture.Decongestants and topical nasal vasoconstrictors.
#DIVING BAROTRAUMA EAR TREATMENT PLUS#
Grade 3 changes pluse hemorrhage within the middle ear (hemotympanum)įree blood in the middle ear plus perforation of the tympanic membrane Gross hemorrhage throughout the tympanic membrane TEED grading system for middle ear barotraumaĮrythema and mild retraction of the tympanic membraneĮrythema of the tympanic membrane with mild or spotty hemorrhage within the membrane.Webber and Rinne for middle ear barotrauma.Herpes zoster oticus (Ramsay Hunt syndrome).Caustic cocktail from rebreathing circuit.Pulmonary barotrauma ( pulmonary overpressurization syndrome).Must be lacking in any other neurologic signs (otherwise consider infarction)ĭifferential Diagnosis Diving Emergencies.Sudden onset of sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, severe vertigo.Pressure difference between middle ear and inner ear can rupture oval or round window.Results from forceful valsalva against an occluded eustachian tube, or rapid descent in diving or aviation.Pain, fullness, vertigo, conductive hearing loss, TM rupture.Results from inability to equalize middle ear pressure.At 2 ATA (10m/33ft) a given gas would be 1/2 it's volume, at 3 ATA (20m/66ft) it would be 1/3 it's volume and so on.Boyles Law applies to the diving body's air filled areas such as lungs, sinuses, middle ear, and states that the volume and pressure of a gas at a given temperature are inversely related.Pascals Law applies to the diving body (without air filled areas such as lungs) states that the pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.Barodentalgia (trapped dental air causing squeeze).Also known as "ear squeeze" - generally seen during scuba diving or air travel.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
